情绪识别模型架构
基于深度学习的驾驶员情绪识别模型,专为车载环境优化,兼顾高精度与实时性
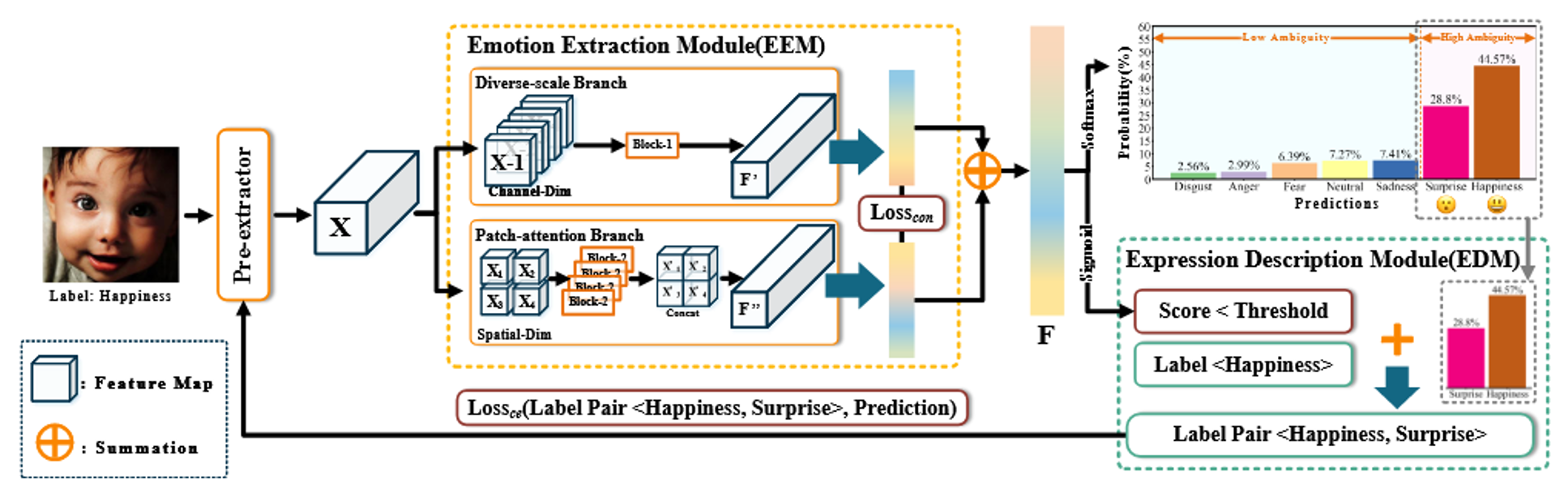
Co-dance with Ambiguity: An Ambiguity-Aware Facial Expression Recognition Framework for More Robustness
Because of the ambiguous and subjective property of the facial expression, the label noise is widely existing in the FER dataset. For this problem, in the training phase, current methods often directly predict whether the label is noised or not, aiming to reduce the contribution of the noised data. However, we argue that this kind of method suffers from the low reliability of such noise data decision operation. It makes that some mistakenly abounded clean data are not utilized sufficiently and some mistakenly kept noised data disturbing the model learning. In this paper, we propose a more reliable noise-label suppression method called ReSup. First, instead of directly predicting noised or not, ReSup makes the noise data decision by modeling the distribution of noise and clean labels simultaneously according to the disagreement between the prediction and the target. Specifically, to achieve optimal distribution modeling, ReSup models the similarity distribution of all samples. To further enhance the reliability of our noise decision results, ReSup uses two networks to jointly achieve noise suppression. Specifically, ReSup utilize the property that two networks are less likely to make the same mistakes, making two networks swap decisions and tending to trust decisions with high agreement. Extensive experiments on popular datasets shows the effectiveness of ReSup.
查看相关论文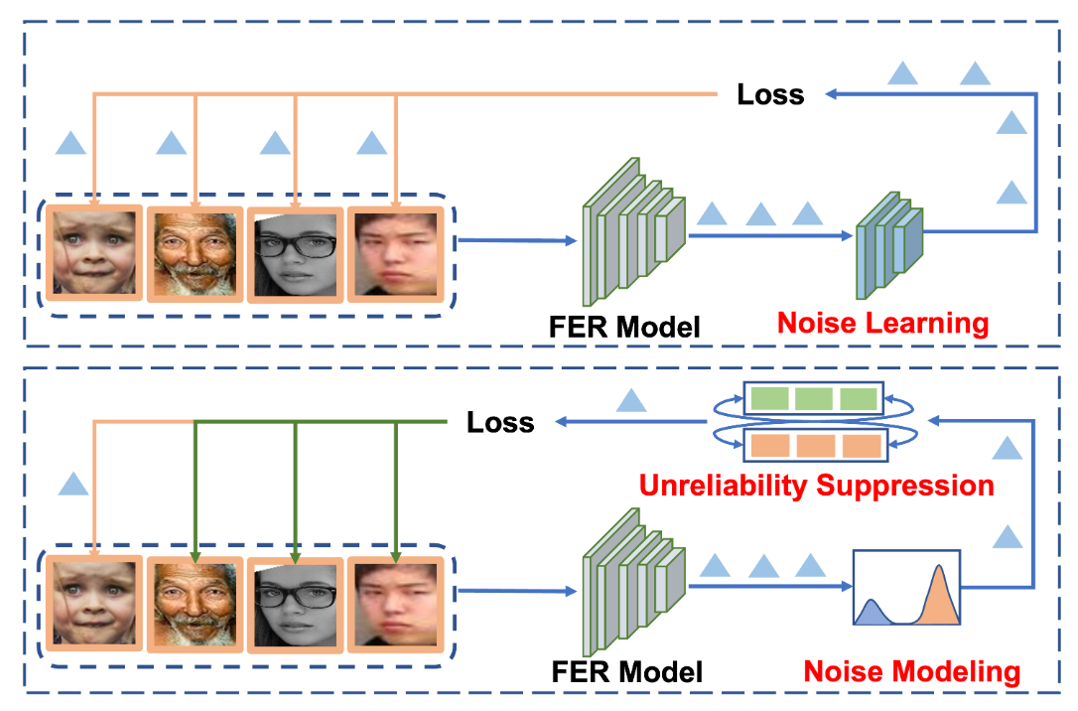
ReSup: Reliable Label Noise Suppression for Facial Expression Recognition
Because of the ambiguous and subjective property of the facial expression, the label noise is widely existing in the FER dataset. For this problem, in the training phase, current methods often directly predict whether the label is noised or not, aiming to reduce the contribution of the noised data. However, we argue that this kind of method suffers from the low reliability of such noise data decision operation. It makes that some mistakenly abounded clean data are not utilized sufficiently and some mistakenly kept noised data disturbing the model learning. In this paper, we propose a more reliable noise-label suppression method called ReSup. First, instead of directly predicting noised or not, ReSup makes the noise data decision by modeling the distribution of noise and clean labels simultaneously according to the disagreement between the prediction and the target. Specifically, to achieve optimal distribution modeling, ReSup models the similarity distribution of all samples. To further enhance the reliability of our noise decision results, ReSup uses two networks to jointly achieve noise suppression. Specifically, ReSup utilize the property that two networks are less likely to make the same mistakes, making two networks swap decisions and tending to trust decisions with high agreement. Extensive experiments on popular datasets shows the effectiveness of ReSup.
查看相关论文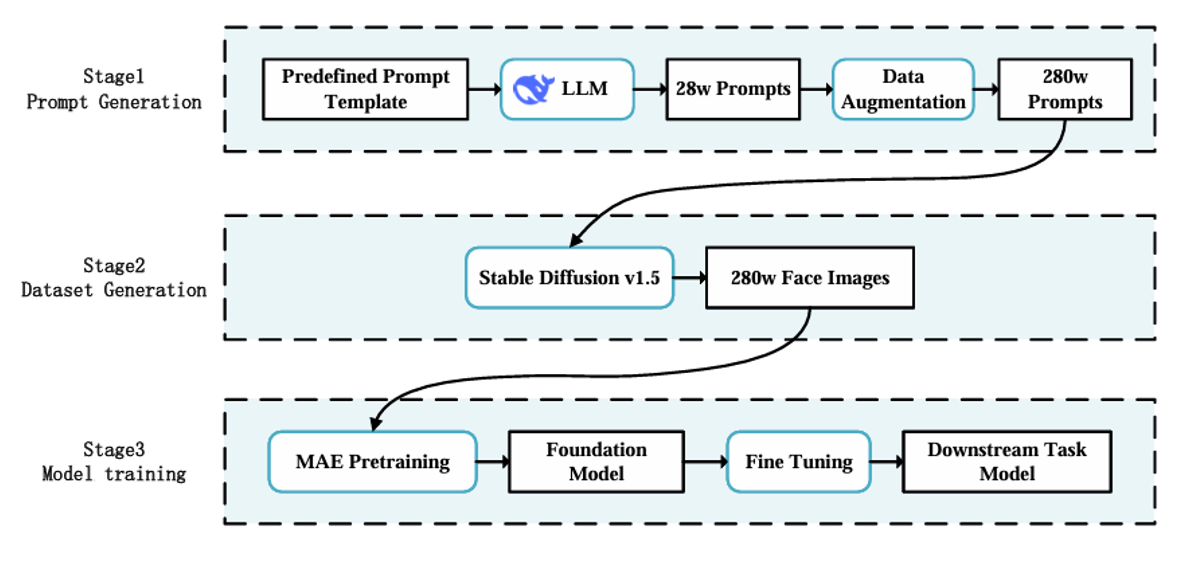
Foundation Model for Facial Recognition
In the field of Facial Expression Recognition (FER), existing real-world datasets generally suffer from label noise and imbalanced data distribution. The former stems from subjective biases in manual annotation and interference in data collection, while the latter is reflected in the high proportion of samples for common expressions such as "happiness" and "neutrality," and the scarcity of minority-class samples like "fear" and "disgust. Both issues limit the model's generalization ability and recognition accuracy.To address this problem, large-scale FER datasets can be generated through an artificially controllable approach, which not only avoids noise and imbalance in real-world data but also ensures sample diversity and standardization. Based on such datasets, unsupervised training can be used to build a general facial recognition model, which can be adapted to downstream tasks such as emotion recognition in smart cabins and emotional feedback in human-computer interaction after fine-tuning.
相关论文还未发表...